

- Home
- Companies
- Bioconservacion SA
- Articles
- Desulfurization and reduction of ...
Desulfurization and reduction of siloxanes in biogas - Case Study
Case Study: MCFC Project at Cetagua (Mataró - Spain)
Reducing the carbon footprint of our society is essential. This can be achieved by capturing and confining anthropogenic CO2 emissions, as well as by replacing fossil fuels with renewable fuels.
MCFCs (Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells) are the only ones capable of doing both. Thanks to their principle of operation, CO2 can be extracted from a gas stream on the cathode side and fuels such as biogas can be converted into electricity on the anode side. However, the degradation caused by the pollutants present in these gases must be addressed.
In this sense the project "MCFC catalyst and stack component degradation and lifetime: Fuel Gas Contaminant effects and Extraction strategies" aims to tackle this problem from two sides:
1) the investigation of the mechanisms of poisoning caused by fuels and to determine precisely the MCFC tolerance limits for long-term endurance;
2) optimization of fuel and gas cleaning to achieve adapted degrees of purification according to the operating conditions and MCFC tolerance.
CETaqua (Centro Tecnológico del Agua), a company belonging to the Suez group was involved in the project, where one of its main objectives was to test on a pilot scale, alternative adsorbent materials to activated carbons that were being conventionally used in most wastewater treatment plants (WWTP).
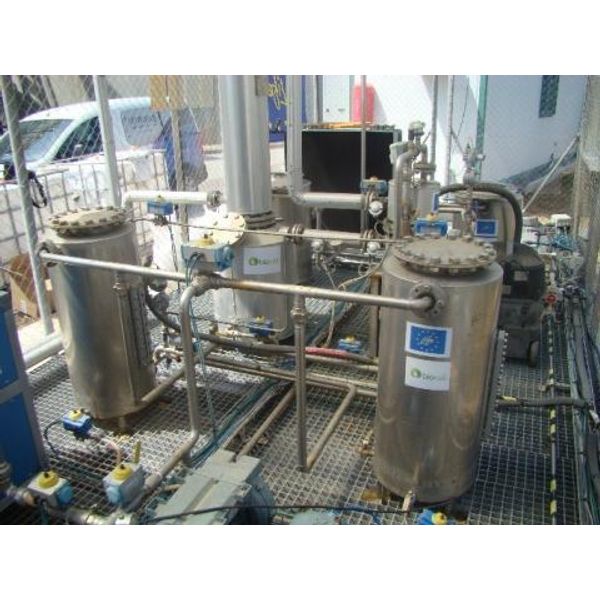

To this end, CETaqua contacted Bioconservacion and a biogas purification project was carried out at the Mataró WWTP (Barcelona), a two-stage system. The system consists of two identical lines composed of a first vessel filled with 3 mm BION SIGMA (formerly Bi-On Fe) to remove H2S and a second step with a vessel filled with 4 mm BION AC for VOCs and extraction siloxanes (Figure 1).
The tests last about half a year and the results were evaluated at a rate of 10Nm3 / h, and the contaminant concentrations were in a range between 700-2000 ppmv and 4-5 mg / m3 for H2S and siloxanes, respectively.
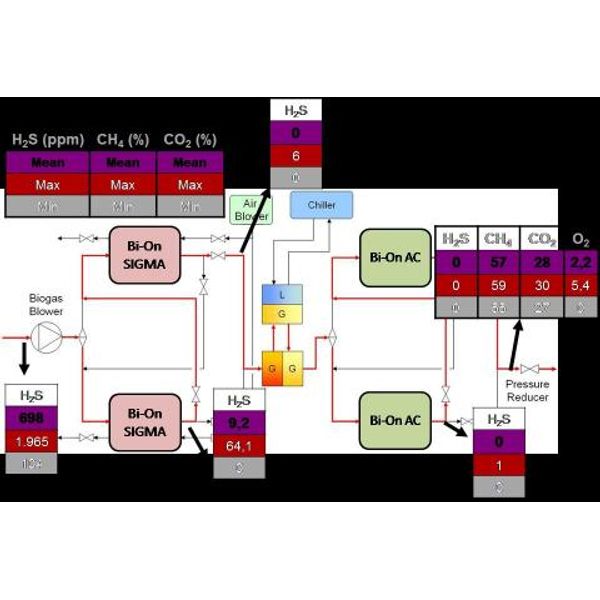
As can be seen, H2S was successfully removed in both lines and only during certain episodes, where peaks were measured, significant amounts of H2S were detected at the outlet of the first stage, but always maintaining removal efficiency values of more than 95% (Figures 2). Either way, the second vessel filled with CA Bi-On, not only removes siloxanes and VOCs, but acted as a polishing stage that resulted in negligible H2S concentrations after the overall purification system.
Figure 3 clearly shows that Bi-On SIGMA was depleted, as both colors can be distinguished before and after use.
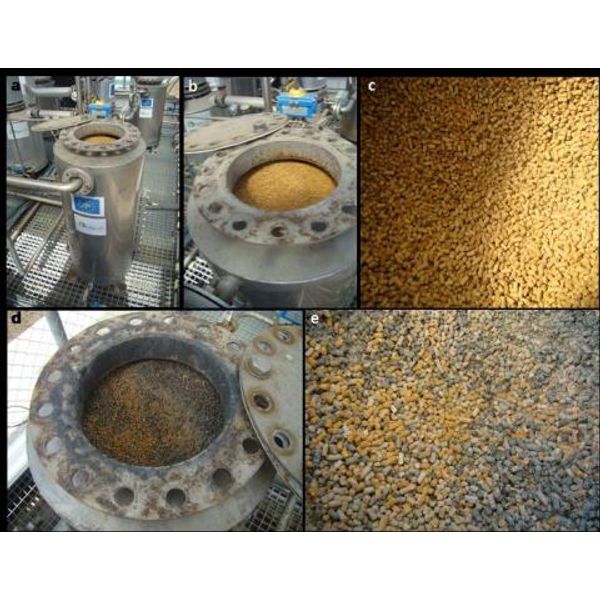

As for siloxanes, BION AC achieves removal efficiency values of about 30%, a value that might seem low, but there is a wide variety of siloxanes and not all of them are effectively removed with the same carbon quality. Therefore, depending on the siloxane to be removed, we could suggest one or another type of carbon. Taking into account that no characterization of siloxanes had been done before, the results obtained must be considered satisfactory.
In summary, biogas purification system was successfully carried out and the biogas could be employed in fuel cells.
