
- Home
- Companies
- Solar Turbines Incorporated (STI)
- Articles
- Kennecott Utah Copper Refinery - 6-MW ...
Kennecott Utah Copper Refinery - 6-MW CHP System - Case Study
Quick Facts
LOCATION: Salt Lake County, Utah
MARKET SECTOR: Primary metals
CHP IN OPERATION SINCE: 2010
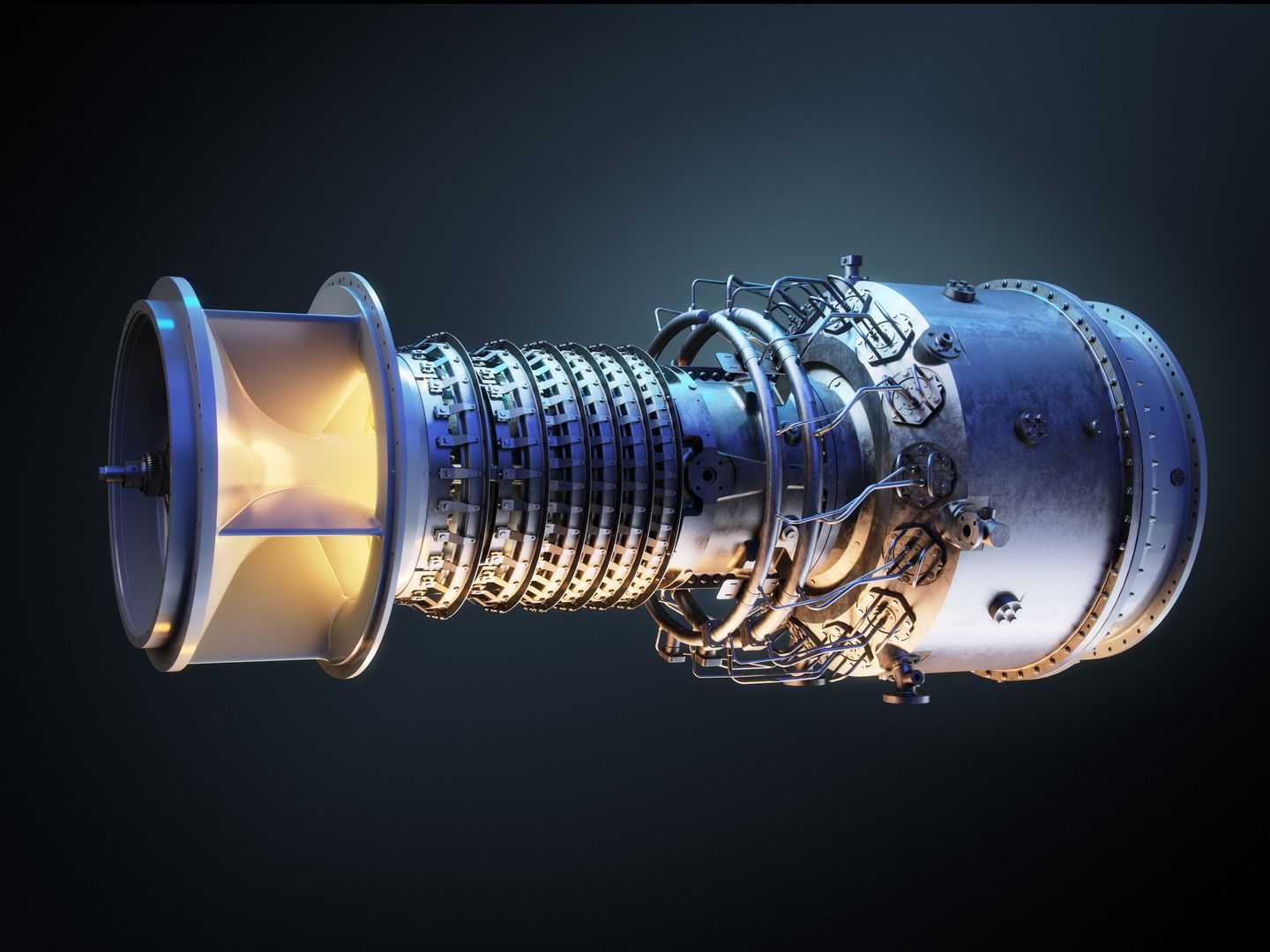
EQUIPMENT: Gas compressor, Solar Taurus 60 turbine generator, HRSG, supplemental burner
ELECTRIC NAMEPLATE CAPACITY: 7.6 MW
AVERAGE ELECTRIC OUTPUT: 6 MW
USE OF THERMAL ENERGY: 70,000 lbs/hour of 50-psi process steam
PRIMARY FUEL: Natural gas (300 psi)
TOTAL EFFICIENCY: 80-82%
TOTAL PROJECT COST: $10 million
ENVIRONMENTAL BENEFITS: Displaces 6 MW of electricity otherwise purchased from the coal-powered grid, plus energy otherwise required to make process steam. NOx emissions reduced by 90%, SO2 emissions by nearly 99%, and annual CO2 emissions by 36,000 tons compared to separate heat and power systems.
Site Description
Kennecott Utah Copper, a subsidiary of Rio Tinto, is the second-largest copper producer in the U.S. It produces about 300,000 tons of copper cathodes per year, which currently supplies about a quarter of the country’s copper. In addition, Kennecott produces 500,000 ounces of gold, 4 million ounces of silver, 30 million pounds of molybdenum, and about 1 million tons of sulfuric acid on an average annual basis.
The copper refinery is the final stage in the copper production cycle, and is located on the west side of Salt Lake County.
Reasons for CHP
A 6-megawatt (MW) combined heat and power (CHP) system installed in 2010 produces more than half of the refinery’s total electricity needs. Waste heat from the CHP is recycled to produce process steam.
CHP is a good technical and economic fit for the refinery because of its steam demand, and it also fits into Kennecott’s larger movement towards improving energy efficiency throughout operations.
