ICAX Ltd products
ICAX - Asphalt Solar Collector
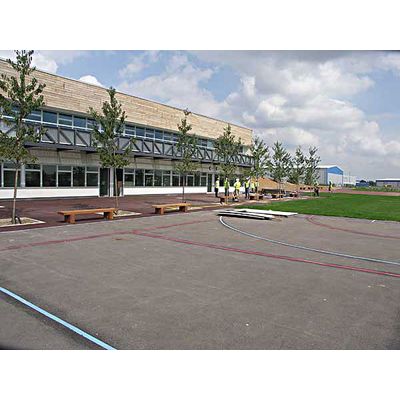
ICAX Limited designed the Asphalt Solar Collector as part of the ICAX Solar Road System for use in Interseasonal Heat Transfer. An Asphalt Solar Collector is an efficient means of collecting a large amount of warmth to raise the temperature of a ThermalBank from the natural temperature of the ground up to over 25°C: solar recharge of the ground. Black roads tend to absorb the heat of the sun up to the point when they radiate heat as quickly as they are absorbing it: the surface temperature of roads in direct sunshine can often reach 15°C higher than the ambient air temperature. ICAX collects heat using fluid circulating through an array of pipes embedded in the surface of the road and deposits it in ThermalBanks constructed beneath the insulated foundation of buildings. The temperature across a large ThermalBank can be increased from its natural temperature of 10°C to over 25°C in the course of the summer months.
ICAX - Asphalt Heat Rejector
There is a tendency for modern buildings to have a high need for cooling. This is particularly significant for high occupancy buildings with passive heat gains from people, lighting, computers and high solar gains from extensive use of glazing in the facade. Many commercial buildings in South East England have annual cooling loads which are larger than the heating loads, even in the cooler months. Supermarkets have high cooling loads from process cooling of food chiller cabinets.
ICAX - Concrete Solar Collector
ICAX Limited designed the Concrete Solar Collector as part of the ICAX Solar Road System for use in Interseasonal Heat Transfer. A Concrete Solar Collector is an efficient means of collecting a large amount of warmth to raise the temperature of a ThermalBank from the natural temperature of the ground up to over 25°C: solar recharge of the ground. Black roads tend to absorb the heat of the sun up to the point when they radiate heat as quickly as they are absorbing it: the surface temperature of roads in direct sunshine can often reach 15°C higher than the ambient air temperature. ICAX collects heat using fluid circulating through an array of pipes embedded in the surface of the road and deposits it in ThermalBanks constructed beneath the insulated foundation of buildings. The temperature across a large ThermalBank can be increased from its natural temperature of 10°C to over 25°C in the course of the summer months.
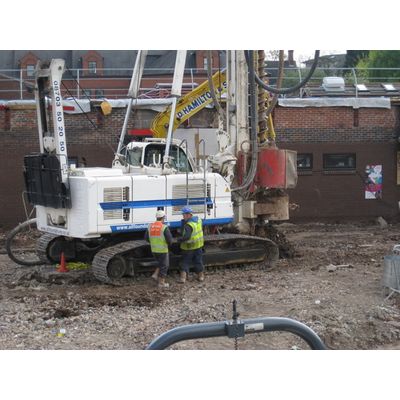
ThermalBanks - Borehole Thermal Energy Storage System
A Thermal Bank is a bank of earth used to store heat energy collected in the summer for use in winter to heat buildings. A Thermal Bank is an integral part of an Interseasonal Heat Transfer system invented, developed and patented by ICAX to answer the need for on site renewable energy without burning fossil fuels.
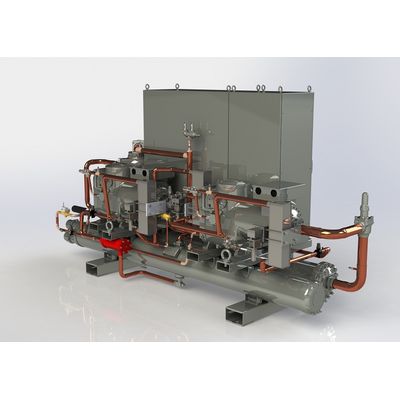
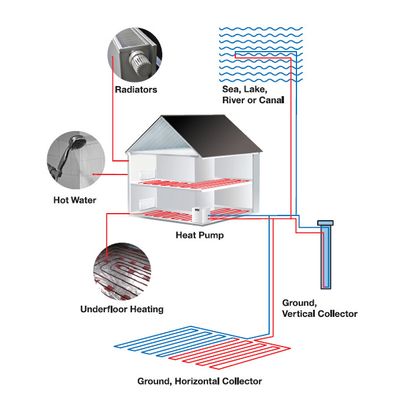
Heat Pump
ICAX - Water Source Heat Pumps
An Open Water Heat Pump system works by recovering the solar energy stored naturally in river water or open water. The water then passes through heat pumps to yield its low grade heat before being returned to the river with a temperature change of 3°C.
ICAX - Air Source Heat Pumps - ASHP
An Air Source Heat Pump (ASHP) can be an efficient means of saving money and saving carbon emissions if carefully designed for space heating of an appropriately designed building.
ICAX - Ground Source Heat Pump
Ground source heat pumps work by absorbing heat from the ground and transferring the heat into buildings – to heat the buildings without burning fossil fuels. The heat pump itself is located in the building and works on the same principles as a domestic fridge: the heat pump in a fridge transfers heat out of the fridge and uses a heat exchanger to disperse the heat from a small radiator at the back of the fridge into the room.
ICAX - Groundwater Heat Pumps
A Groundwater Heat Pump system works by recovering heat stored naturally in groundwater or aquifers. The water passes through heat pumps to yield its low grade heat before being returned to the aquifer at a lower temperature.
ICAX - Domestic Ground Source Heat Pumps
A Ground Source Heat Pump transfers heat from the ground into buildings. Radiation from the sun heats the earth. The earth then stores the heat and maintains, just two metres or so down, a temperature of around 10°C even throughout the winter. A ground source heat pump uses a ground heat exchange loop to tap into this constantly replenished heat store to heat buildings and provide hot water. The technology used is the same as that used in refrigerators. Just as a fridge extracts heat from the food and transfers it into the kitchen, so a ground source heat pump extracts heat from the earth and transfers it into a building.