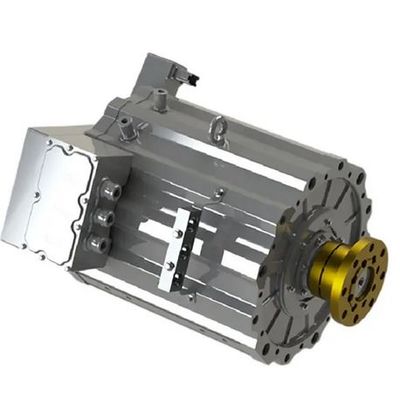
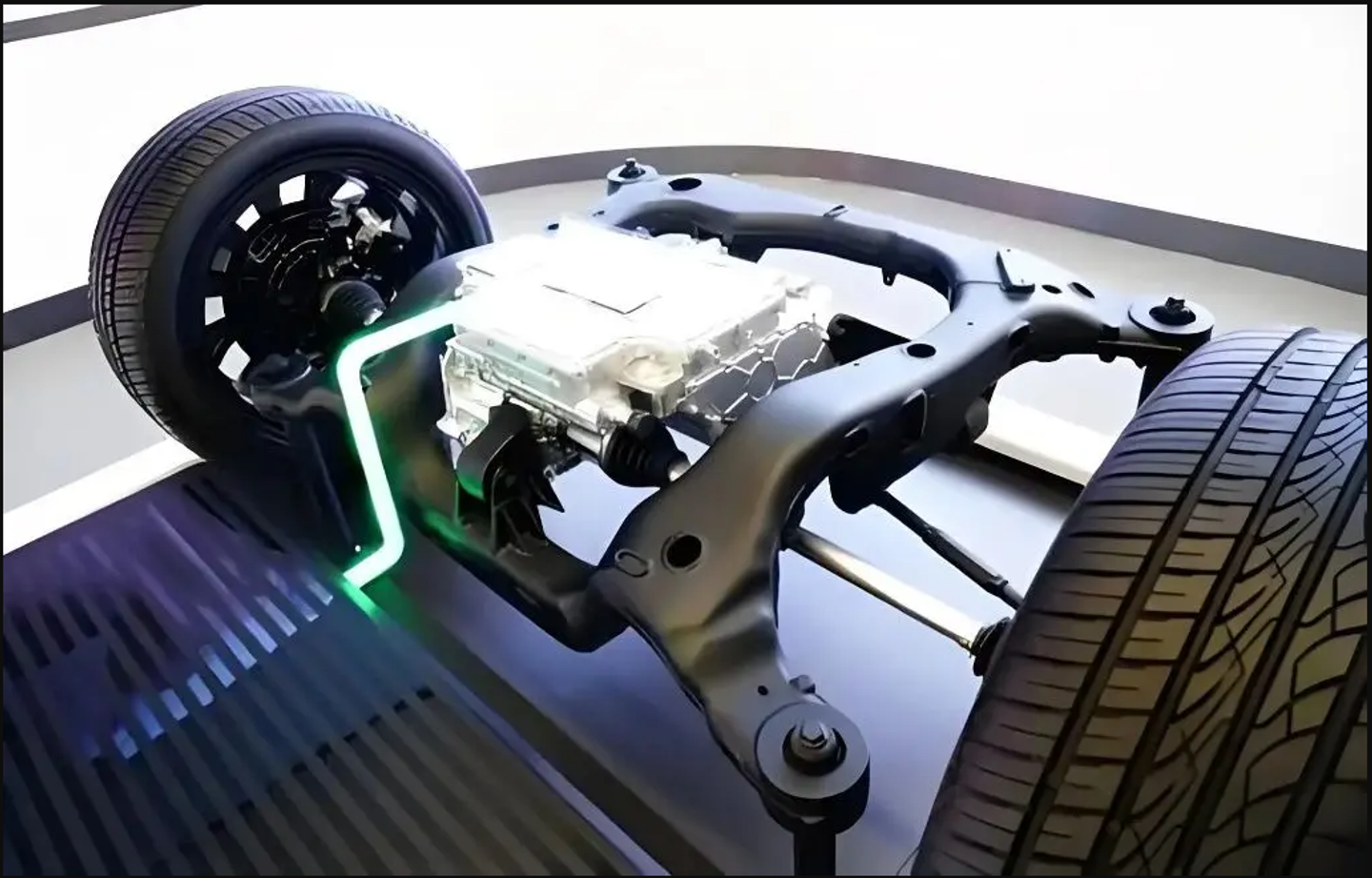


Pumbaaev - Model Gen5 PML080 -Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM ) for Electric Vehicle Drive
The winding form of the motor gradually transitions from round wire to flat wire, with high slot filling rate, short ends, high power density and strong heat dissipation capacity.
The brushless electric motor (PMSM-RRB)uses a permanent magnet to provide excitation (excitation: the magnetic field upon which the motor operatesIt). it is brushless and does not require excitation current to improve the efficiency and power density of the motor.
As early as the 1920s there was the world`s first motor, and this motor rotor part is a permanent magnet, used to generate field excitation. But the permanent magnet material used at that time is natural magnetite ore (FE3O4) , magnetic energy density is very low, with it made of large motor, soon replaced by electric excitation motor. With the development of technology, there are many choices for permanent magnet materials, among which the most excellent is rare earth materials, so the use of rare earth permanent magnet materials called rare earth permanent magnet motor.
Synchronous motor can be divided into two types: non-salient pole motor and salient pole motor. The `laminated steel rotor core` in figure 18 should be the `laminated steel stator core`
Figure 19: salient-pole external excitation synchronous machine (left) , non-salient-pole permanent magnet synchronous machine (PMSM/SMPMSM)(middle) , and salient-pole built-in permanent magnet machine (IPMSM)(right)(6) Centralized and distributed windings
Synchronous motor windings can be distributed or centralized. When the windings are centralized, all wires are in a slot and span one pole, i. e. span is one pole, as can be seen in fig. 18 and Fig. 20(Top) . Distributed windings have a larger span. In the example in figure 19(right) , each winding spans six slots, while in Figure 20(bottom) , the span is 3. In addition, centralized windings of different phases do not overlap, while distributed windings do, as can be clearly seen in figure 20. Centralized windings use less copper and have shorter end windings. In figure 20, the two images on the right show the extent to which the copper end windings are longer than the rotor length. The distributed windings in the lower right picture show the extent to which the end is enlarged. Due to the small number of cross slots in the centralized winding, less copper is required for connecting the windings. Thus centralized windings can be constructed in a more compact manner, using less copper (and thus, less expensive).
Centralised (top) winding vs. distributed (bottom) winding
However, due to the excellent performance of distributed windings, this type of winding is still the main type of winding; compared with centralized windings, the spatial waveform optimization of excitation flux of distributed windings (almost sinusoidal) , therefore, the harmonic content is low and the performance is excellent. The winding mode of distributed winding can produce nearly constant rotating stator magnetic field. As the cost of motor manufacturing is increasing, the pressure on manufacturers is also increasing. As the manufacture of centralized windings is simpler and cheaper, the manufacture of centralized windings is becoming more common.
Permanent Magnet synchronous motor is divided into two ways: one is to control the motor through frequency conversion governor to achieve synchronization, one is to achieve synchronization through asynchronous starting mode.
The brushless electric motor can not be started directly by three-phase AC. Due to the large inertia of the rotor, the magnetic field rotates too fast, and the stationary rotor can not start and rotate with the magnetic field at all.
VVF mode: the power supply of the brushless electric motor is provided by the VF, and the output frequency of the VF rises continuously from 0 to the working frequency at startup, the speed of the motor rises synchronously with the frequency of the inverter. The speed of the motor can be changed by changing the frequency of the inverter.
Asynchronous start-up mode: the start-up and operation of the brushless electric motor is caused by the interaction of the magnetic field generated by the stator winding, rotor squirrel cage winding and permanent magnet. The direct three-phase electric power supply is to install cage winding on the permanent magnet rotor where no speed adjustment is required.
Control of permanent magnet synchronous motor
In order to improve the performance of the permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) control system, make it have faster response speed, higher speed precision and wider speed range, a variety of new control strategies are proposed for permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) control. Permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) control includes vector control, Direct torque control control and intelligent control.
(1)the vector control strategy of PMSM is different from that of asynchronous motor. Because the speed of PMSM is in strict synchronization with the frequency of power supply, its rotor speed is equal to the speed of rotating magnetic field, and the slip is equal to zero. Therefore, it is easier to realize vector control on permanent magnet synchronous motor.
(2)the Direct torque control Direct torque control does not require vector control complicated rotation coordinate transformation and rotor flux orientation. The torque replaces the current as the controlled object, and the voltage vector is the only input to the control system, direct control torque and flux increase or decrease, but torque and flux linkage are not decoupled, the motor model is simplified, no PWM signal generator, simple control structure, small impact of motor parameters changes, excellent dynamic performance is achieved.
(3)In order to improve the control performance and precision of permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) , fuzzy control and neural network control have been applied to the control of PMSM. In the multi-loop control structure, the intelligent controller acts as the speed controller in the outermost loop, pi control and Direct torque control control are still used in inner loop current control and torque control, the main function of the inner loop is to modify the plant characteristics for the control of the outer loop, and the error caused by various disturbances can be controlled or restrained by the outer loop.
In the application of intelligent control in permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) system, the traditional control method can not be completely abandoned.
- Permanent magnet traction drive systems with excellent torque density and minimum loss
- Synchronous machines: cost effective, low loss at low load conditions, thermally stable
- Hybrid machines combining benefits from different machine types to achieve low cost and high performance
- Internal, external and axial rotor geometries can be accommodated
- Zero Emission operation
- Compact design
- High performance density
- NVH optimised design
- Model: PML080
- Cooling Method: Water cooling
- Peak Power: 160KW
- Rated Power: 80KW
- Peak Torque: 1700/2100N.m
- Peak Speed: 4000/3500rpm
- Overall Dimensions: 602×465×503mm
- Applications: Bus&coach City Sanitation
High voltage insulation design
The motor adopts new insulating materials and processes to meet the high switching frequency requirements of SiC controllers for increasingly high-speed motors
High-speed and heavy-duty insulated bearings
The motor design uses insulated bearings, which can meet the design requirements of 24000RPM/min; And it can effectively inhibit the generation of electrical corrosion of bearings
Oil-cooled motor
The motor adopts a high-speed oil-cooled structure, which effectively reduces the rated power after the volume is reduced, which not only improves the efficiency, but also improves the service life of the system
Excellent NVH performance
The motor rotor adopts a segmented inclined pole structure, which effectively optimizes the NVH of the motor system
Excellent NVH performance
The motor rotor adopts a segmented inclined pole structure, which effectively optimizes the NVH of the motor system
