

- Home
- Companies
- Solvay - Soil Treatment Products
- Products
- SOCALand Winnofil - Model PCC - Fine ...

SOCALand Winnofil - Model PCC -Fine Uncoated Calcium Carbonate
SOCAL and Winnofil is produced using the most economic process existing today. Limestone is converted into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide by means of calcination at temperatures in excess of 900°C. To ensure a high level of purity, the calcination process is carried out using natural gas.
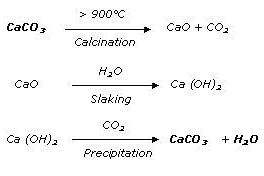
Following total carbonization, a suspension of CaCO3 results. A cake comprising 40% - 60% solid matter (depending on particle diameter) is then obtained by filtration. This filter cake is then dried and subsequently disagglomerated in grinders.
Ultrafine coated grades SOCAL and WINNOFIL are reacted with fatty acids prior to filtration i.e. when still in the suspension stage.
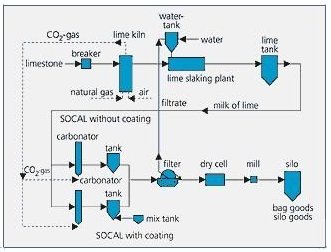
The particle size, as well as the crystal form, is controlled by temperature, concentration of reactants and time.
Depending on the chemical composition of the milk of lime used and on the purifying stages during production: technical as well as foodstuff and pharmaceutical grades can be produced.
Crystallographic shapes of calcium carbonate:
Precipitated Calcium Carbonate is a synthetic calcium carbonate, which can crystallize in different crystal structures like Calcitic Rhombohedral, Calcitic Scalenohedral… The available crystal shapes for Socal and Winnofil are reproduced below

Compared with dry or wet milled natural calcites or chalks, PCC can be distinguished through its finer and more uniform particle sizes, closer particle size distribution and a higher degree of chemical purity.
Characteristics of SOCAL and WINNOFIL:
- Crystal system: Rhombohedral
- Density: 2.71
- Hardness acc. to MOHS: 3
- Free flowing density: 200 – 400 g/L
Reactions with acid
- With mineral acids: exothermic reaction generating combined salts and CO2 gas.
- With organic acids: same kind of reactions, easily forming a superficial coating if the acid is used in a small quantity.
Solubility in water
- Solubility in water containing no carbon dioxide is very small and increases with temperature.
- On the contrary, in water containing CO2 (e.g. once in contact with the air), solubility is noticeably increased and in this instance, decreases with temperature.
- In an atmosphere of CO2, solubility increases one hundred-fold and soluble bicarbonate [Ca(HCO3)2] is formed.
